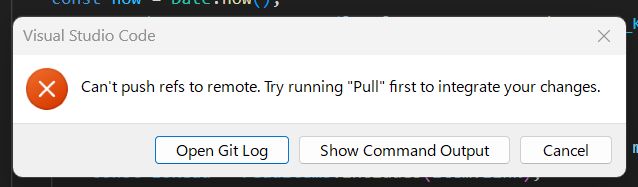
When trying to push to GitHub, you might encounter the following error message:
Updates were rejected because the remote contains work that you do not have locally.This means "The remote repository (GitHub) has new commits that do not exist in your local environment." Git is warning you: "If you push now, the changes on GitHub will be lost, so please pull and merge them first."
Summary: What is happening? The GitHub repository is ahead of your local branch. To resolve this, you must run git pull first to incorporate the differences.
1. The Basic Solution (Solves 90% of cases)
First, update your local environment to the latest state by running pull.
Steps
Run the following command in your VS Code terminal or Git Bash:
git pullOutcome Patterns
- If there are no conflicts: The process completes automatically. You can now run git push successfully.
- If there are conflicts: This happens if the same line in the same file was edited both remotely and locally. You will need to fix this manually (explained below).
2. How to Handle Conflicts
If a conflict occurs during git pull, VS Code (or your editor) will display something like this:
<<<<<<< HEAD
Your changes (Local)
=======
GitHub's changes (Remote)
>>>>>>> origin/mainFix Steps
- Decide which to keep In VS Code, buttons like "Accept Current Change" (Keep local), "Accept Incoming Change" (Keep remote), or "Accept Both Changes" will appear above the code. Click the appropriate one.
- Save the file Once the edits are done, save the file.
- Commit and Push Finalize the changes and push.
git add .
git commit -m "Fix conflict"
git push3. Common Causes
Why does this error happen? Here are the most common patterns:
- Pattern A: Edited directly on GitHub (Most common)
- You edited the README or other files directly in the GitHub browser interface.
- A bot (like GitHub Actions) automatically committed changes.
- Pattern B: Pushed from another PC
- You worked on another computer and pushed changes, but forgot to pull them on your current machine.
This happens frequently in team development, but even in personal projects, it often occurs when you make "quick fixes in the browser" and then work locally.
4. [Last Resort] Force Push
If you think, "I don't care about the changes on GitHub! I want to overwrite them with my local content!" (for example, if you made a mistake in a commit on GitHub), you can force the push.
Warning: Using this command will completely erase the history on GitHub that does not exist locally. In team development, this is strictly prohibited in most cases.
If it is your own personal blog or a repository strictly for yourself, it might be acceptable depending on the situation.
git push --forceSummary
If you see this error, stay calm and try the following steps:
- First, try git pull.
- If there are no issues, run git push.
- If there is a conflict, fix it, then git add -> git commit -> git push.
- (For personal projects only) If it's too much trouble, consider git push –force.